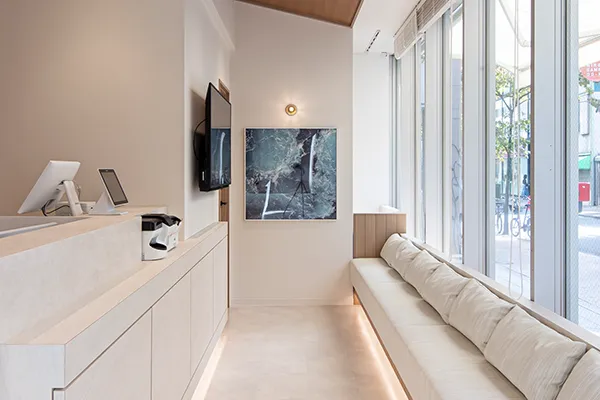
- Because the main language in our clinic is Japanese, while we do accept patients of other nationalities, we may take measures such as using a translation device. If at all possible, we recommend that you bring someone with you who can speak Japanese.
- What to bring on the day (passport, residence card, list of regular medications)
- We only treat patients who are able to attend the clinic
- Persons on short-term tourist visas must basically pay 100% of the cost of treatment themselves (cash only)
- Payment methods: Credit cards accepted, cash payment in Japanese yen only